Articles
General purpose IoT button
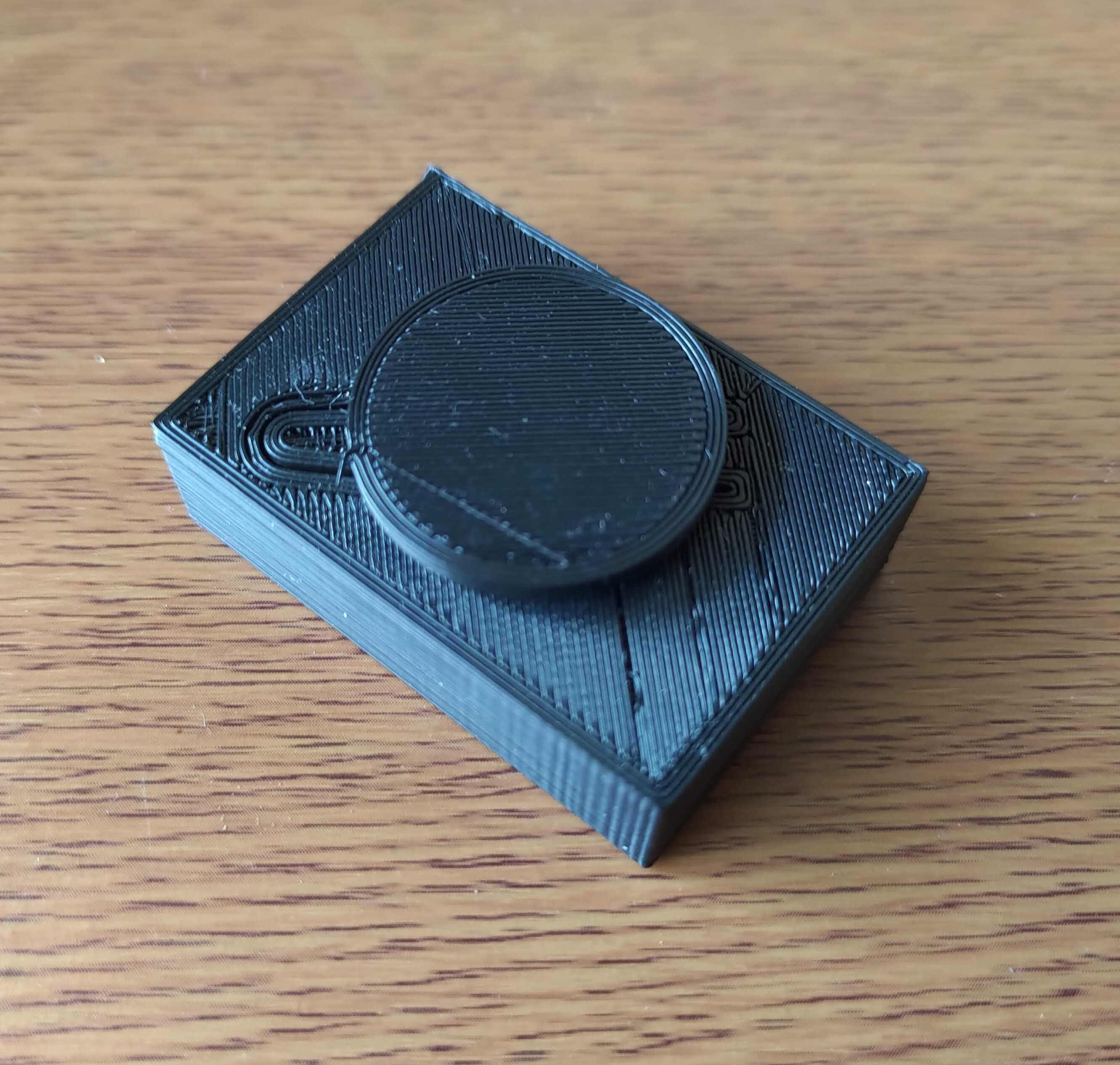
Over the years, I have built multiple IoT devices ranging from AC controllers to ceiling lights. Usually, I would control those devices using my smartphone or computer but sometimes a physical button can be more convenient. Thus, I designed this simple IoT button which publishes MQTT messages when pressed.
Generating certificates for an Aruba Instant AP using pfSense
Aruba IAP can use custom certificates when serving the Web UI over HTTPS. Those certificates can be generated, among others, using pfSense. This can be useful when trying to get rid of browser warnings regarding untrusted HTTPS connections
Generic Kubernetes manifest for web application deployment
Deployment name, container registry and service port are externalized, making this manifest general-purpose
Getting Python's requests library to use a local DNS (Core-DNS, Docker-compose, etc.) while behind a proxy
When using Python's requests library, the requests are send through the proxy set as environment variables. Consequently, if the DNS to be used comes before said proxy, the host might not be resolved. This typically happens when resolving a host in Kubernetes using Core-DNS. If the request first leaves the Kubernetes cluster to reach the proxy, then the DNS server becomes unreachable, making the request fail.
Git store credentials
Having to enter one's credentials for every push to a remote can be annoying. Here is to have git save those credentials for future uses.
GitLab CI
GitLab CI is a feature of GitLab that allows users to have actions triggered upon pushing a repository to it's remote. For example, it can be used to execute all tests defined in the code, containerize the application and deploy it. A popular alternative to GitLab CI is Jenkins.
GitLab CI Microk8s integration
GitLab provides Kubernetes integration out of the box, which means that GitLab CI/CD Pipelines can be used to deploy applications in Kubernetes easily. This guide presents how to integrate a Kubernetes cluster in a GitLab Project and follows Gitlab documentation. For this particular case, the cluster will be that of a Microk8s Kubernetes distribution.
GitLab Microk8s >1.24 certificate based integration

With newer versions of Microk8s, its GitLab integration changes slightly. Here are the key differences
Gitlab CI commands for TF serving
This is an example .gitlab-ci.yml file which can be used to containerize and deploy a tensorflow model
Gitlab CI dealing with credentials
GitLab can automatically dockerize applications using the appropriate CI configuration. However, for obvious security reasons, it is bad practice to include credentials in a git repository. Consequently, the CI pipeline is by default not in a position to include credentials in the dockerized application, which most likely prevents the latter from running as intended.